| // Copyright (c) 2025, the Dart project authors. Please see the AUTHORS file |
| // for details. All rights reserved. Use of this source code is governed by a |
| // BSD-style license that can be found in the LICENSE file. |
| // |
| // API docs from [MDN Web Docs](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web). |
| // Attributions and copyright licensing by Mozilla Contributors is licensed |
| // under [CC-BY-SA 2.5](https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/2.5/. |
| |
| // Generated from Web IDL definitions. |
| |
| // ignore_for_file: unintended_html_in_doc_comment |
| |
| @JS() |
| library; |
| |
| import 'dart:js_interop'; |
| |
| import 'dom.dart'; |
| import 'gamepad.dart'; |
| import 'geometry.dart'; |
| import 'html.dart'; |
| import 'webxr_hand_input.dart'; |
| |
| typedef XRHandedness = String; |
| typedef XRTargetRayMode = String; |
| |
| /// The **`XRSpace`** interface of the |
| /// [WebXR Device API](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/WebXR_Device_API) |
| /// is an abstract interface providing a common basis for every class which |
| /// represents a virtual coordinate system within the virtual world, in which |
| /// its origin corresponds to a physical location. Spatial data in WebXR is |
| /// always expressed relative to an object based upon one of the descendant |
| /// interfaces of `XRSpace`, at the time at which a given [XRFrame] takes place. |
| /// |
| /// Numeric values such as pose positions are thus coordinates in the |
| /// corresponding `XRSpace`, relative to that space's origin. |
| /// |
| /// > [!NOTE] |
| /// > The `XRSpace` interface is never used directly; instead, all spaces are |
| /// > created using one of the interfaces based on `XRSpace`. At this time, |
| /// > those are [XRReferenceSpace], [XRBoundedReferenceSpace], and |
| /// > [XRJointSpace]. |
| /// |
| /// --- |
| /// |
| /// API documentation sourced from |
| /// [MDN Web Docs](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/XRSpace). |
| extension type XRSpace._(JSObject _) implements EventTarget, JSObject {} |
| |
| /// The WebXR Device API's **`XRReferenceSpace`** interface describes the |
| /// coordinate system for a specific tracked entity or object within the virtual |
| /// world using a specified tracking behavior. The tracking behavior is defined |
| /// by the selected [reference space type](#reference_space_types). It expands |
| /// upon the base class, [XRSpace], by adding support for several different |
| /// tracking behaviors as well as to request a new reference space which |
| /// describes the offset transform between the tracked object and another |
| /// location in the world. |
| /// |
| /// All reference spaces—with the sole exception being bounded reference |
| /// spaces—are described using the `XRReferenceSpace` type. Bounded spaces are |
| /// implemented as [XRBoundedReferenceSpace] objects. These are special spaces |
| /// which let you establish a perimeter within which it's "safe" for the viewer |
| /// to move. For XR systems that allow the user to physically move around, such |
| /// as those that track movement with a real-world camera, this boundary |
| /// establishes the edges of the area the user is able to move around in, |
| /// whether due to physical obstacles or due to limitations of the XR hardware. |
| /// See the article |
| /// [Using bounded reference spaces to protect the viewer](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/WebXR_Device_API/Bounded_reference_spaces) |
| /// for more on using boundaries to keep the user from colliding with obstacles |
| /// both physical and virtual. |
| /// |
| /// --- |
| /// |
| /// API documentation sourced from |
| /// [MDN Web Docs](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/XRReferenceSpace). |
| extension type XRReferenceSpace._(JSObject _) implements XRSpace, JSObject { |
| /// The [XRReferenceSpace] |
| /// interface's **`getOffsetReferenceSpace()`** method returns a |
| /// new reference space object which describes the relative difference in |
| /// position between |
| /// the object on which the method is called and a given point in 3D space. |
| /// The |
| /// object returned by `getOffsetReferenceSpace()` is an |
| /// [XRReferenceSpace] if called on an `XRReferenceSpace`, or an |
| /// [XRBoundedReferenceSpace] if called on an object of that type. |
| /// |
| /// In other words, when you have an object in 3D space and need to position |
| /// another object |
| /// relative to that one, you can call `getOffsetReferenceSpace()`, passing |
| /// into |
| /// it the position and orientation you want the second object to have |
| /// _relative to the position and orientation of the object on which you call |
| /// `getOffsetReferenceSpace()`_. |
| /// |
| /// Then, when drawing the scene, you can use the offset reference space to |
| /// not only |
| /// position objects relative to one another, but to apply the needed |
| /// transforms to render |
| /// objects properly based upon the viewer's position. This is demonstrated in |
| /// the example |
| /// [Implementing rotation based on non-XR inputs](#implementing_rotation_based_on_non-xr_inputs), |
| /// which demonstrates a way to |
| /// use this method to let the user use their mouse to pitch and yaw their |
| /// viewing angle. |
| external XRReferenceSpace getOffsetReferenceSpace( |
| XRRigidTransform originOffset); |
| external EventHandler get onreset; |
| external set onreset(EventHandler value); |
| } |
| |
| /// The WebXR Device API's **`XRViewport`** interface provides properties used |
| /// to describe the size and position of the current viewport within the |
| /// [XRWebGLLayer] being used to render the 3D scene. |
| /// |
| /// --- |
| /// |
| /// API documentation sourced from |
| /// [MDN Web Docs](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/XRViewport). |
| extension type XRViewport._(JSObject _) implements JSObject { |
| /// The read-only [XRViewport] interface's |
| /// **`x`** property indicates the offset from the left edge of |
| /// the destination surface (typically a [XRWebGLLayer]) to the left edge of |
| /// the viewport within the surface into which WebXR content is to be |
| /// rendered. The |
| /// viewport's [XRViewport.y] property identifies the `y` |
| /// component of the origin, and its is given by the [XRViewPort.width] |
| /// and [XRViewport.height] properties. |
| external int get x; |
| |
| /// The read-only [XRViewport] interface's |
| /// **`y`** property indicates the offset from the bottom edge of |
| /// the destination surface (typically a [XRWebGLLayer]) to the bottom edge of |
| /// the viewport within the surface into which WebXR content is to be |
| /// rendered. The |
| /// viewport's [XRViewport.x] property identifies the `x` |
| /// component of the origin, and its is given by the [XRViewPort.width] |
| /// and [XRViewport.height] properties. |
| external int get y; |
| |
| /// The read-only [XRViewport] property |
| /// **`width`** specifies the width of the viewport, in pixels, |
| /// onto the drawing surface the 3D scene is to be rendered into. This is |
| /// defined |
| /// using this property along with the viewport's [XRViewport.height] |
| /// and its origin given by its properties [XRViewport.x] and |
| /// [XRViewport.y]. |
| external int get width; |
| |
| /// The read-only [XRViewport] property |
| /// **`height`** specifies the height, in pixels, of the viewport |
| /// onto the drawing surface within which the WebXR view is to be rendered. |
| /// Along |
| /// with [XRViewport.width] and the origin point given by |
| /// [XRViewport.x] and [XRViewport.y], this defines the |
| /// area within which rendered content will be drawn. |
| external int get height; |
| } |
| |
| /// The **`XRRigidTransform`** is a |
| /// [WebXR API](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/WebXR_Device_API) |
| /// interface that represents the 3D geometric transform described by a position |
| /// and orientation. |
| /// |
| /// `XRRigidTransform` is used to specify transforms throughout the WebXR APIs, |
| /// including: |
| /// |
| /// - The offset and orientation relative to the parent reference space to use |
| /// when creating a new reference space with |
| /// [XRReferenceSpace.getOffsetReferenceSpace]. |
| /// - The [XRView.transform] of an [XRView]. |
| /// - The [XRPose.transform] of an [XRPose]. |
| /// - The [XRReferenceSpaceEvent] event's [XRReferenceSpaceEvent.transform] |
| /// property, as found in the [XRReferenceSpace.reset_event] event received by |
| /// an [XRReferenceSpace]. |
| /// |
| /// Using `XRRigidTransform` in these places rather than bare arrays that |
| /// provide the matrix data has an advantage. It automatically computes the |
| /// inverse of the transform and even caches it making subsequent requests |
| /// significantly faster. |
| /// |
| /// --- |
| /// |
| /// API documentation sourced from |
| /// [MDN Web Docs](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/XRRigidTransform). |
| extension type XRRigidTransform._(JSObject _) implements JSObject { |
| external factory XRRigidTransform([ |
| DOMPointInit position, |
| DOMPointInit orientation, |
| ]); |
| |
| /// The read-only [XRRigidTransform] property |
| /// **`position`** is a [DOMPointReadOnly] object which |
| /// provides the 3D point, specified in meters, describing the translation |
| /// component of the |
| /// transform. |
| external DOMPointReadOnly get position; |
| |
| /// The read-only [XRRigidTransform] property |
| /// **`orientation`** is a [DOMPointReadOnly] |
| /// containing a normalized (also called a **unit |
| /// quaternion** or **[versor](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Versor)**) |
| /// specifying the rotational component of the transform represented by the |
| /// object. |
| /// If you specify a quaternion whose length is not exactly 1.0 meters, it |
| /// will be |
| /// normalized for you. |
| external DOMPointReadOnly get orientation; |
| |
| /// The read-only [XRRigidTransform] property **`matrix`** returns the |
| /// transform matrix represented by the object. The returned matrix can then |
| /// be premultiplied with a column vector to rotate the vector by the 3D |
| /// rotation specified by the [XRRigidTransform.orientation], then translate |
| /// it by the [XRRigidTransform.position]. |
| external JSFloat32Array get matrix; |
| |
| /// The read-only **`inverse`** property |
| /// of the [XRRigidTransform] interface returns another |
| /// [XRRigidTransform] object which is the inverse of its owning |
| /// transform. That is, you can always get the inverse of any |
| /// `XRRigidTransform` using its `inverse` property, instead of having |
| /// to explicitly generate it. |
| external XRRigidTransform get inverse; |
| } |
| |
| /// `XRPose` is a |
| /// [WebXR API](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/WebXR_Device_API) |
| /// interface representing a position and orientation in the 3D space, relative |
| /// to the [XRSpace] within which it resides. The `XRSpace`—which is either an |
| /// [XRReferenceSpace] or an [XRBoundedReferenceSpace]—defines the coordinate |
| /// system used for the pose and, in the case of an [XRViewerPose], its |
| /// underlying views. |
| /// |
| /// To obtain the `XRPose` for the `XRSpace` used as the local coordinate system |
| /// of an object, call [XRFrame.getPose], specifying that local `XRSpace` and |
| /// the space to which you wish to convert: |
| /// |
| /// ```js |
| /// thePose = xrFrame.getPose(localSpace, baseSpace); |
| /// ``` |
| /// |
| /// The pose for a viewer (or camera) is represented by the [XRViewerPose] |
| /// subclass of `XRPose`. This is obtained using [XRFrame.getViewerPose] instead |
| /// of `getPose()`, specifying a reference space which has been adjusted to |
| /// position and orient the node to provide the desired viewing position and |
| /// angle: |
| /// |
| /// ```js |
| /// viewerPose = xrFrame.getViewerPose(adjReferenceSpace); |
| /// ``` |
| /// |
| /// Here, `adjReferenceSpace` is a reference space which has been updated using |
| /// the base frame of reference for the frame and any adjustments needed to |
| /// position the viewer based on movement or rotation which is being supplied |
| /// from a source other than the XR device, such as keyboard or mouse inputs. |
| /// |
| /// See the article [Movement, orientation, and |
| /// motion](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/WebXR_Device_API/Movement_and_motion) |
| /// for further details and an example with thorough explanations of what's |
| /// going on. |
| /// |
| /// --- |
| /// |
| /// API documentation sourced from |
| /// [MDN Web Docs](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/XRPose). |
| extension type XRPose._(JSObject _) implements JSObject { |
| /// The `transform` read-only attribute of the |
| /// [XRPose] interface is a [XRRigidTransform] object providing |
| /// the position and orientation of the pose relative to the base [XRSpace] |
| /// as specified when the pose was obtained by calling |
| /// [XRFrame.getPose]. |
| external XRRigidTransform get transform; |
| |
| /// The `linearVelocity` read-only property of the |
| /// [XRPose] interface is a [DOMPointReadOnly] describing |
| /// the linear velocity in meters per second relative to the base |
| /// [XRSpace]. |
| external DOMPointReadOnly? get linearVelocity; |
| |
| /// The `angularVelocity` read-only property of the |
| /// [XRPose] interface is a [DOMPointReadOnly] describing |
| /// the angular velocity in radians per second relative to the base |
| /// [XRSpace]. |
| external DOMPointReadOnly? get angularVelocity; |
| |
| /// The `emulatedPosition` read-only attribute of the |
| /// [XRPose] interface is a Boolean value indicating whether or not both the |
| /// [XRRigidTransform.position] component of the pose's |
| /// [XRPose.transform] is directly taken from the XR device, or |
| /// it's simulated or computed based on other sources. |
| external bool get emulatedPosition; |
| } |
| |
| /// The WebXR Device API interface **`XRViewerPose`** represents the pose (the |
| /// position and orientation) of a viewer's point of view on the scene. Each |
| /// `XRViewerPose` can have multiple views to represent, for example, the slight |
| /// separation between the left and right eye. |
| /// |
| /// This view can represent anything from the point-of-view of a user's XR |
| /// headset to the viewpoint represented by a player's movement of an avatar |
| /// using mouse and keyboard, presented on the screen, to a virtual camera |
| /// capturing the scene for a spectator. |
| /// |
| /// --- |
| /// |
| /// API documentation sourced from |
| /// [MDN Web Docs](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/XRViewerPose). |
| extension type XRViewerPose._(JSObject _) implements XRPose, JSObject { |
| /// The read-only [XRViewerPose] property **`views`** |
| /// returns an array which contains every [XRView] which must be rendered in |
| /// order to fully represent the scene from the viewpoint defined by the |
| /// viewer pose. For |
| /// monoscopic devices, this array contains a single view. |
| /// |
| /// > [!WARNING] |
| /// > There is no guarantee that the number of views will |
| /// > remain constant over the lifetime of an [XRSession]. For each frame, you |
| /// > should always use the current length of this array rather than caching |
| /// > the value. |
| /// |
| /// Stereo views require two views to render properly, with the left eye's |
| /// view having its |
| /// [XRView.eye] set to the string `left` and the right eye's |
| /// view a value of `right`. |
| external JSArray<JSObject> get views; |
| } |
| |
| /// The [WebXR Device |
| /// API's](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/WebXR_Device_API) |
| /// **`XRInputSource`** interface describes a single source of control input |
| /// which is part of the user's WebXR-compatible virtual or augmented reality |
| /// system. The device is specific to the platform being used, but provides the |
| /// direction in which it is being aimed and optionally may generate events if |
| /// the user triggers performs actions using the device. |
| /// |
| /// --- |
| /// |
| /// API documentation sourced from |
| /// [MDN Web Docs](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/XRInputSource). |
| extension type XRInputSource._(JSObject _) implements JSObject { |
| /// The read-only [XRInputSource] property |
| /// **`handedness`** indicates which of the user's hands the WebXR |
| /// input source is associated with, or if it's not associated with a hand at |
| /// all. |
| external XRHandedness get handedness; |
| |
| /// The read-only [XRInputSource] |
| /// property **`targetRayMode`** indicates the method by which the |
| /// target ray for the input source should be generated and how it should be |
| /// presented to |
| /// the user. |
| /// |
| /// Typically a target ray is drawn from the source of the targeting system |
| /// along the target ray in the direction in which the user is looking or |
| /// pointing. The style of the ray is generally up to you, as is the method |
| /// for indicating the endpoint of the ray. The targeted point or object might |
| /// be indicated by drawing a shape or highlighting the targeted surface or |
| /// object. |
| /// |
| /// A target ray emitted by a hand controller: |
| /// |
| /// 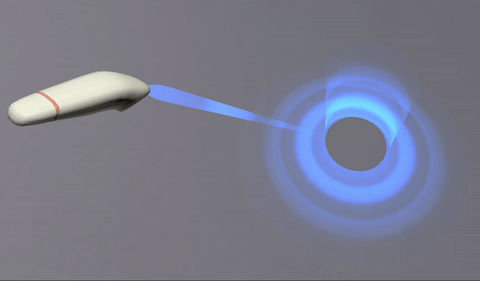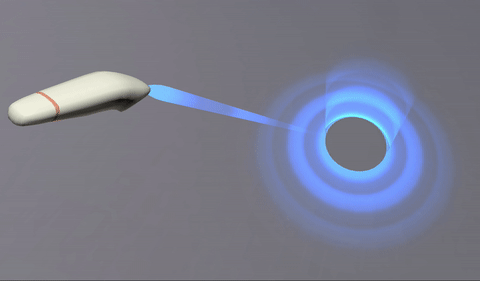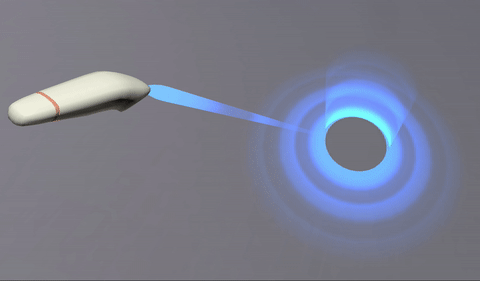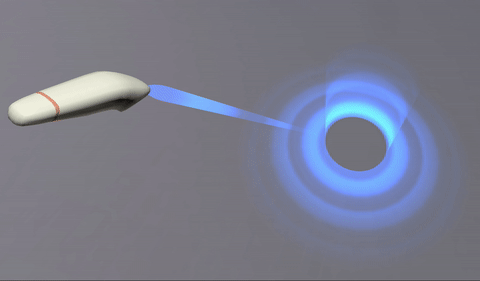 |
| /// |
| /// The target ray can be anything from a simple line (ideally fading over |
| /// distance) to an animated effect, such as the science-fiction "phaser" |
| /// style shown in the screenshot above. |
| external XRTargetRayMode get targetRayMode; |
| |
| /// The read-only [XRInputSource] property |
| /// **`targetRaySpace`** returns an [XRSpace] |
| /// (typically an [XRReferenceSpace]) representing the position and |
| /// orientation of the target ray in the virtual space. Its native origin |
| /// tracks |
| /// the position of the origin point of the target ray, and its orientation |
| /// indicates the |
| /// orientation of the controller device itself. These values, interpreted in |
| /// the context of |
| /// the input source's [XRInputSource.targetRayMode], can be |
| /// used both to fully interpret the device as an input source. |
| /// |
| /// To obtain an `XRSpace` representing the input controller's position and |
| /// orientation in virtual space, use the [XRInputSource.gripSpace] property. |
| external XRSpace get targetRaySpace; |
| |
| /// The read-only [XRInputSource] property **`gripSpace`** returns an |
| /// [XRSpace] whose native origin tracks the pose used to render virtual |
| /// objects so they appear to be held in (or part of) the user's hand. For |
| /// example, if a user were holding a virtual straight rod, the native origin |
| /// of this `XRSpace` would be located at the approximate center of mass of |
| /// the user's fist. |
| external XRSpace? get gripSpace; |
| |
| /// The read-only [XRInputSource] property **`profiles`** returns an array of |
| /// strings, each describing a configuration profile for the input source. The |
| /// profile strings are listed in order of specificity, with the most specific |
| /// profile listed first. |
| /// |
| /// > [!NOTE] |
| /// > The `profiles` list is always empty when the WebXR |
| /// > session is in inline mode. |
| external JSArray<JSString> get profiles; |
| |
| /// The read-only [XRInputSource] property **`gamepad`** returns a [Gamepad] |
| /// object describing the state of the buttons and axes on the XR input |
| /// source, if it is a gamepad or comparable device. If the device isn't a |
| /// gamepad-like device, this property's value is `null`. |
| /// |
| /// The [Gamepad] instance returned behaves as described by the |
| /// [Gamepad API](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/Gamepad_API). |
| /// However, there are a few things to note: |
| /// |
| /// - `Gamepad` instances belonging to `XRInputSource` are not included in the |
| /// array returned by [navigator.getGamepads]. Gamepads are strictly |
| /// associated with the WebXR hardware and are not general-purpose gaming |
| /// devices. |
| /// - [Gamepad.id] is an empty string (`""`) |
| /// - [Gamepad.index] is `-1` |
| /// - [Gamepad.connected] is `true` until the `XRInputSource` is removed from |
| /// the list of active XR input sources or the [XRSession] is ended. |
| /// - If an axis reported by [Gamepad.axes] represents an axis of a touchpad, |
| /// the value is 0 when the associated [GamepadButton.touched] property is |
| /// `false`. |
| /// - [Gamepad.mapping] returns "xr-standard". |
| external Gamepad? get gamepad; |
| |
| /// The read-only **`hand`** property of the [XRInputSource] interface is a |
| /// [XRHand] object providing access to a hand-tracking device. |
| external XRHand? get hand; |
| } |
| |
| /// The |
| /// [WebXR Device API](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/WebXR_Device_API)'s |
| /// **`XRSessionEvent`** interface describes an event which indicates the change |
| /// of the state of an [XRSession]. These events occur, for example, when the |
| /// session ends or the visibility of its context changes. |
| /// |
| /// --- |
| /// |
| /// API documentation sourced from |
| /// [MDN Web Docs](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/XRSessionEvent). |
| extension type XRSessionEvent._(JSObject _) implements Event, JSObject { |
| external factory XRSessionEvent( |
| String type, |
| XRSessionEventInit eventInitDict, |
| ); |
| |
| /// The read-only [XRSessionEvent] interface's |
| /// **`session`** property indicates which |
| /// [XRSession] the event is about. |
| external JSObject get session; |
| } |
| extension type XRSessionEventInit._(JSObject _) implements EventInit, JSObject { |
| external factory XRSessionEventInit({ |
| bool bubbles, |
| bool cancelable, |
| bool composed, |
| required JSObject session, |
| }); |
| |
| external JSObject get session; |
| external set session(JSObject value); |
| } |
| |
| /// The |
| /// [WebXR Device API](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/WebXR_Device_API)'s |
| /// **`XRInputSourceEvent`** interface describes an event which has occurred on |
| /// a WebXR user input device such as a hand controller, gaze tracking system, |
| /// or motion tracking system. More specifically, they represent a change in the |
| /// state of an [XRInputSource]. |
| /// |
| /// To learn more about handling inputs in a WebXR project, see the article |
| /// [Inputs and input sources](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/WebXR_Device_API/Inputs). |
| /// |
| /// --- |
| /// |
| /// API documentation sourced from |
| /// [MDN Web Docs](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/XRInputSourceEvent). |
| extension type XRInputSourceEvent._(JSObject _) implements Event, JSObject { |
| external factory XRInputSourceEvent( |
| String type, |
| XRInputSourceEventInit eventInitDict, |
| ); |
| |
| /// The read-only [XRInputSourceEvent] property |
| /// **`frame`** specifies an [XRFrame] object |
| /// representing the event frame during which a |
| /// [WebXR](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/WebXR_Device_API) |
| /// user input occurred. |
| /// This may thus be an event which occurred in the past rather than a current |
| /// or impending |
| /// event. |
| external JSObject get frame; |
| |
| /// The [XRInputSourceEvent] interface's read-only |
| /// **`inputSource`** property specifies the |
| /// [XRInputSource] which generated the input event. This information |
| /// lets you handle the event appropriately given the particulars of the user |
| /// input device |
| /// being manipulated. |
| external XRInputSource get inputSource; |
| } |
| extension type XRInputSourceEventInit._(JSObject _) |
| implements EventInit, JSObject { |
| external factory XRInputSourceEventInit({ |
| bool bubbles, |
| bool cancelable, |
| bool composed, |
| required JSObject frame, |
| required XRInputSource inputSource, |
| }); |
| |
| external JSObject get frame; |
| external set frame(JSObject value); |
| external XRInputSource get inputSource; |
| external set inputSource(XRInputSource value); |
| } |
| |
| /// The WebXR Device API interface **`XRInputSourcesChangeEvent`** is used to |
| /// represent the [XRSession.inputsourceschange_event] event sent to an |
| /// [XRSession] when the set of available WebXR input controllers changes. |
| /// |
| /// --- |
| /// |
| /// API documentation sourced from |
| /// [MDN Web Docs](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/XRInputSourcesChangeEvent). |
| extension type XRInputSourcesChangeEvent._(JSObject _) |
| implements Event, JSObject { |
| external factory XRInputSourcesChangeEvent( |
| String type, |
| XRInputSourcesChangeEventInit eventInitDict, |
| ); |
| |
| /// The [XRInputSourcesChangeEvent] property |
| /// `session` specifies the |
| /// [XRSession] to which the input source list change event applies. |
| external JSObject get session; |
| |
| /// The read-only [XRInputSourcesChangeEvent] |
| /// property `added` is a list of zero or |
| /// more input sources, each identified using an [XRInputSource] object, |
| /// which have been newly made available for use. |
| external JSArray<XRInputSource> get added; |
| |
| /// The read-only [XRInputSourcesChangeEvent] property `removed` is an array |
| /// of |
| /// zero or more [XRInputSource] objects representing the input sources that |
| /// have been removed from the [XRSession]. |
| external JSArray<XRInputSource> get removed; |
| } |
| extension type XRInputSourcesChangeEventInit._(JSObject _) |
| implements EventInit, JSObject { |
| external factory XRInputSourcesChangeEventInit({ |
| bool bubbles, |
| bool cancelable, |
| bool composed, |
| required JSObject session, |
| required JSArray<XRInputSource> added, |
| required JSArray<XRInputSource> removed, |
| }); |
| |
| external JSObject get session; |
| external set session(JSObject value); |
| external JSArray<XRInputSource> get added; |
| external set added(JSArray<XRInputSource> value); |
| external JSArray<XRInputSource> get removed; |
| external set removed(JSArray<XRInputSource> value); |
| } |
| |
| /// The |
| /// [WebXR Device API](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/WebXR_Device_API) |
| /// interface **`XRReferenceSpaceEvent`** represents an event sent to an |
| /// [XRReferenceSpace]. Currently, the only event that uses this type is the |
| /// [XRReferenceSpace.reset_event] event. |
| /// |
| /// --- |
| /// |
| /// API documentation sourced from |
| /// [MDN Web Docs](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/XRReferenceSpaceEvent). |
| extension type XRReferenceSpaceEvent._(JSObject _) implements Event, JSObject { |
| external factory XRReferenceSpaceEvent( |
| String type, |
| XRReferenceSpaceEventInit eventInitDict, |
| ); |
| |
| /// The read-only [XRReferenceSpaceEvent] property |
| /// **`referenceSpace`** specifies the reference space which is the |
| /// originator of the event. |
| external XRReferenceSpace get referenceSpace; |
| |
| /// The read-only [XRReferenceSpaceEvent] property |
| /// **`transform`** indicates the position and orientation of the |
| /// affected [XRReferenceSpaceEvent.referenceSpace]'s |
| /// native origin after the changes the event represents are applied. The |
| /// `transform` is defined using the old coordinate system, which allows it to |
| /// be |
| /// used to convert coordinates from the pre-event coordinate system to the |
| /// post-event |
| /// coordinate system. |
| external XRRigidTransform? get transform; |
| } |
| extension type XRReferenceSpaceEventInit._(JSObject _) |
| implements EventInit, JSObject { |
| external factory XRReferenceSpaceEventInit({ |
| bool bubbles, |
| bool cancelable, |
| bool composed, |
| required XRReferenceSpace referenceSpace, |
| XRRigidTransform? transform, |
| }); |
| |
| external XRReferenceSpace get referenceSpace; |
| external set referenceSpace(XRReferenceSpace value); |
| external XRRigidTransform? get transform; |
| external set transform(XRRigidTransform? value); |
| } |